The greenhouse effect
Earth's climate is the result of a balance between the amount of incoming energy from the sun, and energy being radiated out into space.Incoming solar radiation strikes Earth's atmosphere in the form of visible light, plus ultraviolet and infrared radiation, according to NASA's Earth Observatory.Ultraviolet radiation has a higher energy level than visible light, and infrared radiation has a weaker energy level. Some of the sun's incoming radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere, the oceans and the surface of the Earth.Much of it, however, is reflected back out to space as low-energy IR radiation. For Earth's temperature to remain stable, the amount of incoming solar radiation should be roughly equal to the amount of IR radiation leaving the atmosphere. According to NASA satellite measurements, the atmosphere radiates thermal IR energy equivalent to 59 percent of the incoming solar energy.As Earth's atmosphere changes, however, the amount of IR radiation leaving the atmosphere also changes. Since the Industrial Revolution, the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gasoline have greatly increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, according to NASA's Earth Observatory.Along with other gases like methane and nitrous oxide, CO2 acts like a blanket, absorbing IR radiation and preventing it from leaving the atmosphere. The net effect causes the gradual heating of Earth's atmosphere and surface. [Related: Effects of Global Warming]This is called the "greenhouse effect" because a similar process occurs in a greenhouse: Relatively high-energy UV and visible radiation penetrate the glass> and roof of a greenhouse, but weaker IR radiation isn't able to pass out through the glass. The trapped IR radiation keeps the greenhouse warm, even in the coldest winter weather.
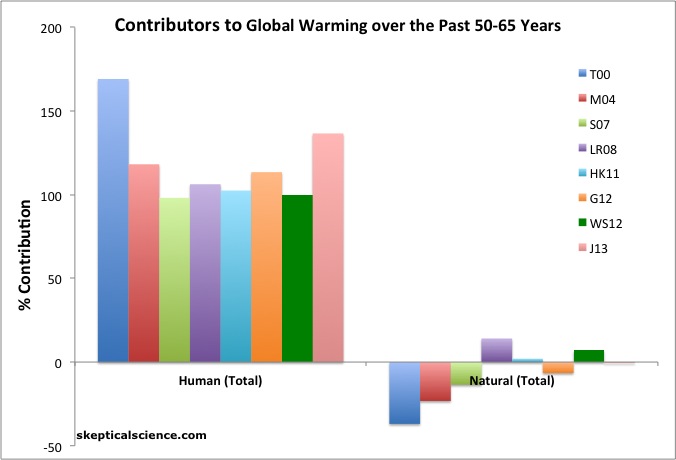
Natural causes vs. human causes
Earth's historic climate changes have included ice ages, warming periods and other fluctuations in climate over many centuries. Some of these historical changes can be attributed to changes in the amount of solar radiation hitting the planet. A drop in solar activity, for example, is believed to have caused the "Little Ice Age," a period of unusually colder climate that lasted from about 1650 to 1850, according to NASA. However, there is no evidence that any increase in solar radiation could be responsible for the steady increase in global temperatures that scientists are now recording, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).In other words, natural causes cannot be held responsible for global warming. "There is no scientific debate on this point," the NOAA website states.Indeed, virtually every credible source of scientific research from around the world indicates that human causes, primarily the burning of fossil fuels and the subsequent increase in atmospheric CO2 levels, are responsible for global warming. Some of these organizations are the American Medical Association, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, American Association for the Advancement of Science, Ecological Society of Australia, American Chemical Society, Geological Society of London, American Geophysical Union, International Arctic Science Committee, American Meteorological Society, American Physical Society, and The Geological Society of America. Over 197 international organizations agree on this point."In all honesty, anthropogenic (human-caused) climate change is not a scientific debate, it is a political/economic debate," Werne said. According to Werne, the relevant question is not, "Is there human-induced climate change?" The question that we should be focused on is, if anything, "What should we do about human-induce climate change?"